Solana, the new kid on the block, is full of innovation, and is expected to shake the blockchain world. The platform incorporated innovative features which allows it to operate up to 50,000 transactions per second.
How is this all possible, and how does Solana work? Keep on reading to understand what the future of blockchain may look like.
- Solana (SOL) history and evolution
- What exactly is Solana?
- How does Solana work?
- What applications run on Solana?
- Who are Solana’s competitors?
- Solana’s milestone includes 250+ partners
- What are the predictions for SOL’s price?
- Solana’s token distribution
- How to buy SOL?
- Solana: a potential market disruptor
- Frequently asked questions
Solana (SOL) history and evolution
What is Solana (SOL), and how did it come to life?
Anatoly Yakovenko, a former contributor to Qualcomm and Dropbox, founded and announced the platform in 2017 when he published the Solana whitepaper. He is a software engineer with experience in compression algorithms and distributed systems. Together with Eric Williams and Solana’s CTO, Greg Fitzgerald, the team aims to make Solana a trustless and distributed protocol to deal with the traditional issues that exist on the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains.
The Solana whitepaper is the first written reference of proof-of-history, described as a new way of timekeeping for the distributed systems on the blockchain.
The team released the Solana platform testnet in February 2018. The company behind the platform, Solana Labs, was initially called Loom. Later, the name changed to avoid any confusion with Loom Network, which is a multichain interoperability solution.
Solana raised more than $5 million from two seed rounds prior to series A. In 2019, Solana Labs completed a $20 million series A funding round led by Multicoin Capital. After its launch auction on CoinList, Solana collected another $1.76 million.
The beta mainnet was launched in March 2020, offering basic transaction capabilities and smart contracts.
Currently, the Solana team has earned its experience by working for the world’s top companies (Apple, Qualcomm, Intel, Google, Microsoft, Twitter, Dropbox, and others). So far, Solana has received attention from many investors, including Multicoin Capital, Foundation Capital, SLOW Capital, CMCC Global, Abstract Ventures, and many more.
At the moment, Solana Labs is the main contributor to the network. The Solana Foundation, a non-profit foundation, actively engages in funding and developing the community’s initiatives.
What exactly is Solana?

Decentralized transactions are possible thanks to the blockchain technology. But the tech we use to transfer cryptocurrencies has a major issue — it’s slow. To put things into perspective, let’s consider the Ethereum network, which can process about 15 transactions per second, compared to the tens of thousands on Visa’s network.
And this is exactly what Solana aims to change for the better. So, what is Solana?
Solana is a programmable blockchain that strives to perform high-speed transactions without losing its core feature, decentralisation. The network uses a novel mechanism called the proof-of-history. SOL, the blockchain’s native token, is used for transaction fees and can also be staked. Solana is a direct competitor to the Ethereum network.
What is a programmable blockchain?
Unlike Bitcoin, which is mainly a huge and immutable ledger, Solana employs smart contracts. These smart contracts are bits of code that trigger actions upon the fulfillment of certain conditions.
Ethereum uses the smart contract feature to deploy decentralized applications (dApps). However, the sheer volume of these self-executing contracts clogged the network.
Consider Ethereum’s comparatively low tps and the large number of smart contracts. The network is slow, has huge transfer fees, and has a huge carbon footprint, as it still operates on the proof-of-work consensus.
Until Ethereum 2.0 fully rolls out, it should leave room for next-gen blockchains to get a share of the dapp market. ETH 2.0 is due to happen in 2022. So far, Solana is the fastest programmable blockchain.
Solana functions on an adapted proof-of-stake consensus model, on top of which state-of-the-art core innovations were deployed.
What makes Solana so fast, is this combo of eight innovative features:
- Proof-of-history
- Tower BFT
- Gulf Stream
- Turbine
- Sealevel
- Pipelining
- Cloudbreak
- Archivers
PoH: What is proof-of-history?

Solana blockchain uses the proof-of-history (PoH) algorithm, which is not a consensus mechanism but a cryptographic clock. PoH makes the entire network more efficient and faster because nodes do not have to communicate to validate a block. Instead, they all have to agree on the time order of the events registered on the chain.
By having historical records of transactions and events on the blockchain, the system can easily keep track of the ordering of the events.
The PoH is achieved thanks to nodes, as each has its own clock, and it’s the main reason for the network’s efficiency.
On the other hand, Bitcoin utilizes the proof-of-work consensus. This requires miners to validate transactions and produce new bitcoins with each new block. Miners must cooperate to achieve consensus, such as establishing when a transaction took place.
The creator of Solana noted in its whitepaper the essential feature of the proof-of-work, which Bitcoin is utilizing — the ability to function as a decentralized clock.
In traditional centralized systems, there is no need for a clock because all nodes of the system can trust that the timestamps are accurate.
As the creator of Solana explained, the PoH is a historical record that proves that an event took place at a specific moment in time. Imagine you take a photo of today’s printed newspaper and post it online. By utilizing PoH, Solana’s blockchain is able to handle more transactions, making the platform scalable and more efficient.
Tower BFT: A practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance optimized for PoH
Solana implements a practical Byzantine fault tolerance, in short pBFT, which is optimised for PoH. The tower BFT is an algorithm that uses the PoH as the cryptographic clock to help it reach consensus without having to send a flood of communication between the nodes. This algorithm helps drastically improve the transaction speed.
Turbine: The protocol for block propagation
Another component of this high-speed blockchain is the turbine protocol, which packs data that requires transferring between the nodes into smaller data packets. Transmitting data in smaller increments helps with the bandwidth issues and increases the network’s processing speed.
Sealevel: Concurring smart contracts
Solana’s efficient runtime is also aided by the Sealevel engine, which allows the processing of transactions in parallel. This is a foundational development in the blockchain industry, as Solana is the first blockchain to be able to perform parallel processing for the same instruction but having different inputs.
Gulf Stream: Solana’s mempool management solution
Gulf Stream is the Solana solution to reduce the unconfirmed transaction pool. The system pushes transaction catching and forwarding to the end of the network. This allows validators to reduce confirmation times, execute transactions ahead of time, and reduce the memory load coming from the unconfirmed transaction pool. Gulf Stream enables Solana to reach 50,000 transactions per second.
Pipelining: Transaction processing unit to achieve single node efficiency
The pipelining process is an optimised way of processing the stream of input data, which needs to be processed in sequential steps. Solana’s CTO compared the pipelining process to the way we do laundry. The clothes go through the process of washing, drying and folding, and each of these steps must be performed in this order, but by different units. This model is commonly used in CU design, and it enables transactions to be quickly validated and replicated to all nodes of the network.
Cloudbreak: Solana’s horizontally scaled state architecture
Solana uses memory-mapped files and sequential operations to aid the network’s scalability. Cloudbreak is the data structure that allows the sequential writes and concurrent reads between the 32 threads that the modern SSD supports.
Archivers: Solana’s distributed ledger store
Archivers are used for storing data. They download the data from the consensus validators. The PoH technology allows the implementation of proof-of-replication (PoRep), for batch verification, across millions of Replicator nodes around the world. Archivers tell the network how many bytes they have available for storage. Based on the total available storage of Archivers and the number of Replicator identities, the network divides the ledger into the right pieces to match the replication rate and fault tolerance. Archivers are rewarded ~3% of inflation for the storing effort.
How does Solana work?
Solana is the world’s first web scalable blockchain. The platform’s permissionless blockchain can generate a throughput of 50,000 TPS due to its one-of-a-kind architecture.
Solana is designed to be the fastest blockchain on the market. It employs eight core features (PoH, Tower BFT, Gulf Stream, Turbine, Sealevel, Pipelining, Cloudbreak, Archivers) that enable it to achieve unseen transaction speeds.
Solana uses a PoS consensus mechanism, aided by the Tower BFT consensus.
The Tower BFT enables the network to reach consensus by enforcing a universal time source called proof-of-history. This creates a permanent reference for all the nodes of the network. Don’t confuse proof-of-history (PoH), the network’s permissionless clock, for a consensus mechanism.
The proof-of-history is a decentralized clock that helps secure the blockchain and is one of the eight core innovations of Solana. The tower BFT uses the permissionless clock to accelerate transactions. The transaction parallelization system, Sealevel, enables smart contracts to run simultaneously, by employing the available GPUs and SSDs.
The Gulf Stream feature is the memory pool system, often called mempool. It helps forward the transactions to validators before the finalization of previous transactions. This helps maximize transaction speed.
In a nutshell, Solana’s processes function like this:
- Receives the translation input on the ledger
- The ledger sequences and orders the messages so that they can be processed by other nodes in an efficient manner
- The same ledger executes current state transactions and stores it in the RAM
- The ledger published the transactions and signature of the final state to Verifiers (these are the replication nodes)
- Verifiers execute the same transactions on the copy of the state and publish their signature of the state when it receives confirmation
- Published confirmations will be the votes for the consensus mechanism
What applications run on Solana?
Now that you have a better understanding of what is Solana, you might be wondering what apps can run on the Solana network.
Solana is a programmable blockchain due to its ability to interact with smart contracts, just like Ethereum. Smart contracts support a range of decentralized applications (DApps), such as NFT markets, DeFi games, and DEXs.
The most popular Solana apps are decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending apps. The network can also support wrapped assets and stablecoins, such as USD Coin. You can find the entire Solana ecosystem here.
Who are Solana’s competitors?
Most permissionless blockchains see Solana as a potential competitor, as it is a viable alternative to older smart contracts blockchains. Many compare Solana to Ethereum, which is the first blockchain-based server platform. The main advantage is that the platform can process up to 50,000 TPS, while Ethereum’s rate is between 15 and 45 TPS.
When comparing in size and history development, Solana’s competitors count SKALE Labs, 1Token, ARK, and Cindx. But the project’s constant improvement and design differentiate it from all the existing blockchains.
Solana’s milestone includes 250+ partners
Solana launched its mainnet beta network in March 2020. Since then, its native coin, SOL, got to be one of the top 10 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. Although the network offers complete functionalities, the developers are still working to improve the network’s features.
Solana already has over 250 projects and partners, including USDC, Chainlink, BSN, and Serum. The team of Solana is confident that scalability for DApps is no longer an issue and aims to bring in partners and capital to help them onboard a billion users.
Solana Labs plans to further accelerate platform building and plans to launch an investing and trading desk for the network. You can follow Solana’s team developments on GitHub.
What are the predictions for SOL’s price?
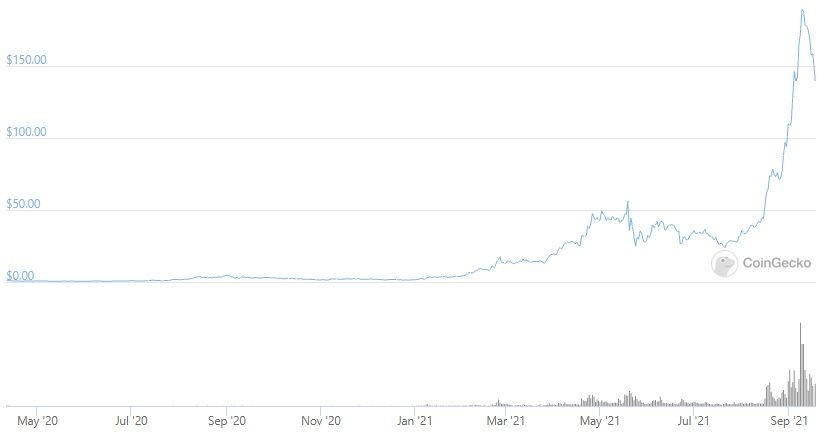
The overall project development and projects that joined Solana contributed to the positive market sentiment. Solana’s native token (SOL) is used for transaction fees and stalking.
The protocol burns all fees paid in SOL, which makes it a deflationary mechanism and helps incentivize users to stake SOL directly from their compatible crypto wallets. This leads to a more secure blockchain.
As of September 2021, Solana’s native token (SOL) is ranking as the 7th cryptocurrency by market capitalization, having a total of 296,831,588.35 circulating tokens.
Given the many successful partnerships, SOL has registered a 66000% surge in price. The all-time high is $214.96, which was reached on September 9, 2021. Investors can also increase their returns by staking SOL.
Solana’s token distribution
As of September 2021, SOL has a circulating supply of $296.69M.
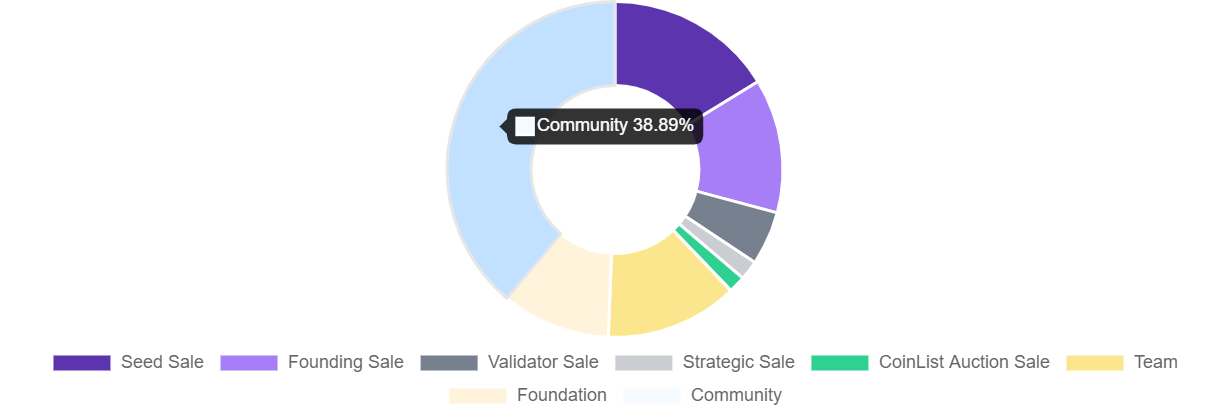
The SOL token supply distribution:
- Seed Sale tokens comprise 16.23% of the total token supply.
- Founding Sale tokens comprise 12.92% of the total token supply.
- Validator Sale tokens comprise 5.18% of the total token supply.
- Strategic Sale tokens comprise 1.88% of the total token supply.
- CoinList Auction Sale tokens comprise 1.64% of the total token supply.
- Team tokens comprise 12.79% of the total token supply.
- Foundation tokens comprise 10.46% of the total token supply.
- Community tokens comprise 38.89% of the total token supply.
The Swiss Foundation, which has an independent board, holds the community tokens. These are used for marketing and grants. The Foundation’s tokens are in Coinbase Custody and cold wallets. The team’s funds are in a USD bank account.
Funds received from the token sales are allocated as follows:
- 3.00% Partnerships.
- 3.00% Marketing.
- 35.00% Team.
- 35.00% Development.
- 12.00% Professional Services & Legal.
- 3.00% Taxes.
- 6.00% Office Rent.
- 3.00% Others.
How to buy SOL?
Solana picks the interest of buyers from all over the world, given its rapid business development and growth. Each day, more crypto exchanges are listing SOL for trading against fiat or other cryptos. Investors can buy SOL on Binance, Bitfinex, FTX, Coinbase and others. SOL can also be used for staking.
Solana: a potential market disruptor
Solana has the potential to disrupt the DApp ecosystem with its next-gen capabilities. The platform is an upgraded blockchain that solves many of the issues that well-known blockchain experienced. Ethereum 2.0 is still some way out, so there’s a chance that Solana could find a strong foothold in the market.
Frequently asked questions
What is Solana?
How does Solana process transactions?
What are some use cases for Solana?
Trusted
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




